Summary
Clan
This family is a member of clan (CL00012), which contains the following 3 members:
SAM SAM-I-IV SAM-IVNote on Riboswitches
This Rfam family SAM (RF00162) represents an aptamer domain of a full riboswitch SAM riboswitch aptamer (S box leader). Riboswitches are non-coding RNA structures that regulate gene expression in response to ligand. Each riboswitch has two main parts: the aptamer domain and the expression platform. The aptamer domain is highly conserved to precisely bind its ligand. However, the expression platform has multiple modes of gene regulation, which introduces sequence and structure variability that increases difficulty in its detection through covariance model searching. For more information see the original publications.
Wikipedia annotation Edit Wikipedia article
The Rfam group coordinates the annotation of Rfam families in Wikipedia. This family is described by a Wikipedia entry SAM riboswitch (S box leader). More...
This page is based on a Wikipedia article. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
Sequences
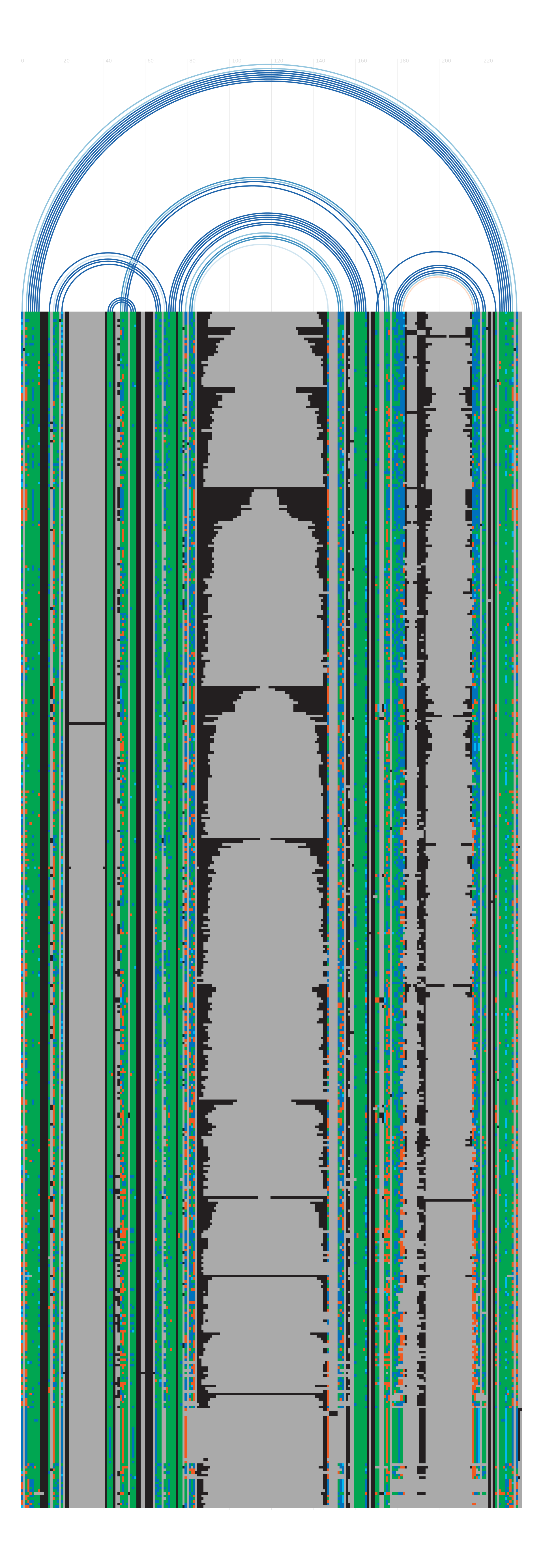
Alignment
Seed alignment view
Download
Download a gzip-compressed, Stockholm-format file containing the seed alignment for this family. You may find RALEE useful when viewing sequence alignments.
Submit a new alignment
We're happy receive updated seed alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Secondary structure
Species distribution
Sunburst controls
HideWeight segments by...
Change the size of the sunburst
Colour assignments
 Archea
Archea
|
 Eukaryota
Eukaryota
|
 Bacteria
Bacteria
|
 Other sequences
Other sequences
|
 Viruses
Viruses
|
 Unclassified
Unclassified
|
 Viroids
Viroids
|
 Unclassified sequence
Unclassified sequence
|
Selections
Click on a node to select that node and its sub-tree.
Clear selection
This visualisation provides a simple graphical representation of the distribution of this family across species. You can find the original interactive tree in the adjacent tab. More...
Tree controls
HideThe tree shows the occurrence of this RNA across different species. More...
Loading...
Please note: for large trees this can take some time. While the tree is loading, you can safely switch away from this tab but if you browse away from the family page entirely, the tree will not be loaded.
Trees
This page displays the predicted phylogenetic tree for the alignment. More...
Note: You can also download the data file for the seed tree.
Structures
For those sequences which have a structure in the Protein DataBank, we generate a mapping between EMBL, PDB and Rfam coordinate systems. The table below shows the structures on which the SAM family has been found.
Loading structure mapping...
Motif matches
There are 2 motifs which match this family.
This section shows the Rfam motifs that match sequences within the seed alignment of this family. Users should be aware that the motifs are structural constructs and do not necessarily conform to taxonomic boundaries in the way that Rfam families do. More...
| Original order | Motif Accession | Motif Description | Number of Hits | Fraction of Hits | Sum of Bits | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | RM00008 | GNRA tetraloop | 86 | 0.188 | 1007.8 |
|
| 7 | RM00010 | Kink turn 1, 3' bulge | 272 | 0.595 | 3383.0 |
|
References
This section shows the database cross-references that we have for this Rfam family.
Literature references
-
Grundy FJ, Henkin TM Mol Microbiol 1998;30:737-749. The S box regulon: a new global transcription termination control system for methionine and cysteine biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria. PUBMED:10094622
-
Winkler WC, Nahvi A, Sudarsan N, Barrick JE, Breaker RR Nat Struct Biol 2003;10:701-707. An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding S-adenosylmethionine. PUBMED:12910260
-
Epshtein V, Mironov AS, Nudler E Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:5052-5056. The riboswitch-mediated control of sulfur metabolism in bacteria. PUBMED:12702767
-
Rodionov DA, Vitreschak AG, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS Nucleic Acids Res 2004;32:3340-3353. Comparative genomics of the methionine metabolism in Gram-positive bacteria: a variety of regulatory systems. PUBMED:15215334
-
Montange RK, Batey RT Nature. 2006;441:1172-1175. Structure of the S-adenosylmethionine riboswitch regulatory mRNA element. PUBMED:16810258
-
Montange RK, Mondragon E, van Tyne D, Garst AD, Ceres P, Batey RT J Mol Biol. 2010;396:761-772. Discrimination between closely related cellular metabolites by the SAM-I riboswitch. PUBMED:20006621
-
Stoddard CD, Montange RK, Hennelly SP, Rambo RP, Sanbonmatsu KY, Batey RT Structure. 2010;18:787-797. Free state conformational sampling of the SAM-I riboswitch aptamer domain. PUBMED:20637415
-
Lu C, Ding F, Chowdhury A, Pradhan V, Tomsic J, Holmes WM, Henkin TM, Ke A J Mol Biol. 2010;404:803-818. SAM recognition and conformational switching mechanism in the Bacillus subtilis yitJ S box/SAM-I riboswitch. PUBMED:20951706
-
Baird NJ, Zhang J, Hamma T, Ferre-D'Amare AR RNA. 2012;18:759-770. YbxF and YlxQ are bacterial homologs of L7Ae and bind K-turns but not K-loops. PUBMED:22355167
-
Schroeder KT, Daldrop P, McPhee SA, Lilley DM RNA. 2012;18:1257-1266. Structure and folding of a rare, natural kink turn in RNA with an A*A pair at the 2b*2n position. PUBMED:22539525
-
Daldrop P, Lilley DM RNA. 2013;19:357-364. The plasticity of a structural motif in RNA: structural polymorphism of a kink turn as a function of its environment. PUBMED:23325110
-
Huang L, Wang J, Lilley DM Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:5390-5398. A critical base pair in k-turns determines the conformational class adopted, and correlates with biological function. PUBMED:27016741
-
Huang L, Liao X, Li M, Wang J, Peng X, Wilson TJ, Lilley DMJ Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49:5916-5924. Structure and folding of four putative kink turns identified in structured RNA species in a test of structural prediction rules. PUBMED:33978763
External database links
| Gene Ontology: | GO:0010468 (regulation of gene expression); |
| Sequence Ontology: | SO:0000035 (riboswitch); |
Curation and family details
This section shows the detailed information about the Rfam family. We're happy to receive updated or improved alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Curation
| Seed source | Grundy F, Henkin T, PMID:10094622 | ||||||
| Structure source | Published; PMID:10094622 | ||||||
| Type | Cis-reg; riboswitch; | ||||||
| Author |
Griffiths-Jones SR ,
Gardner PP ,
Gardner PP ,
Ontiveros-Palacios N ,
Ontiveros-Palacios N
|
||||||
| Alignment details |
|
Model information
| Build commands |
cmbuild -F CM SEED
cmcalibrate --mpi CM
|
| Search command |
cmsearch --cpu 4 --verbose --nohmmonly -T 30.00 -Z 2958934 CM SEQDB
|
| Gathering cutoff | 44.4 |
| Trusted cutoff | 44.4 |
| Noise cutoff | 44.3 |
| Covariance model | Download |
 Loading...
Loading...