Getting started
Sequence search
Annotate your sequences with RNA families and visualise their secondary structure using R2DT
Downloads
Download covariance models, FASTA sequences, database dumps, previous releases, and more
Help
Access Rfam using the API and public MySQL database, or learn how to annotate genomes using Infernal
Announcements
Citing Rfam
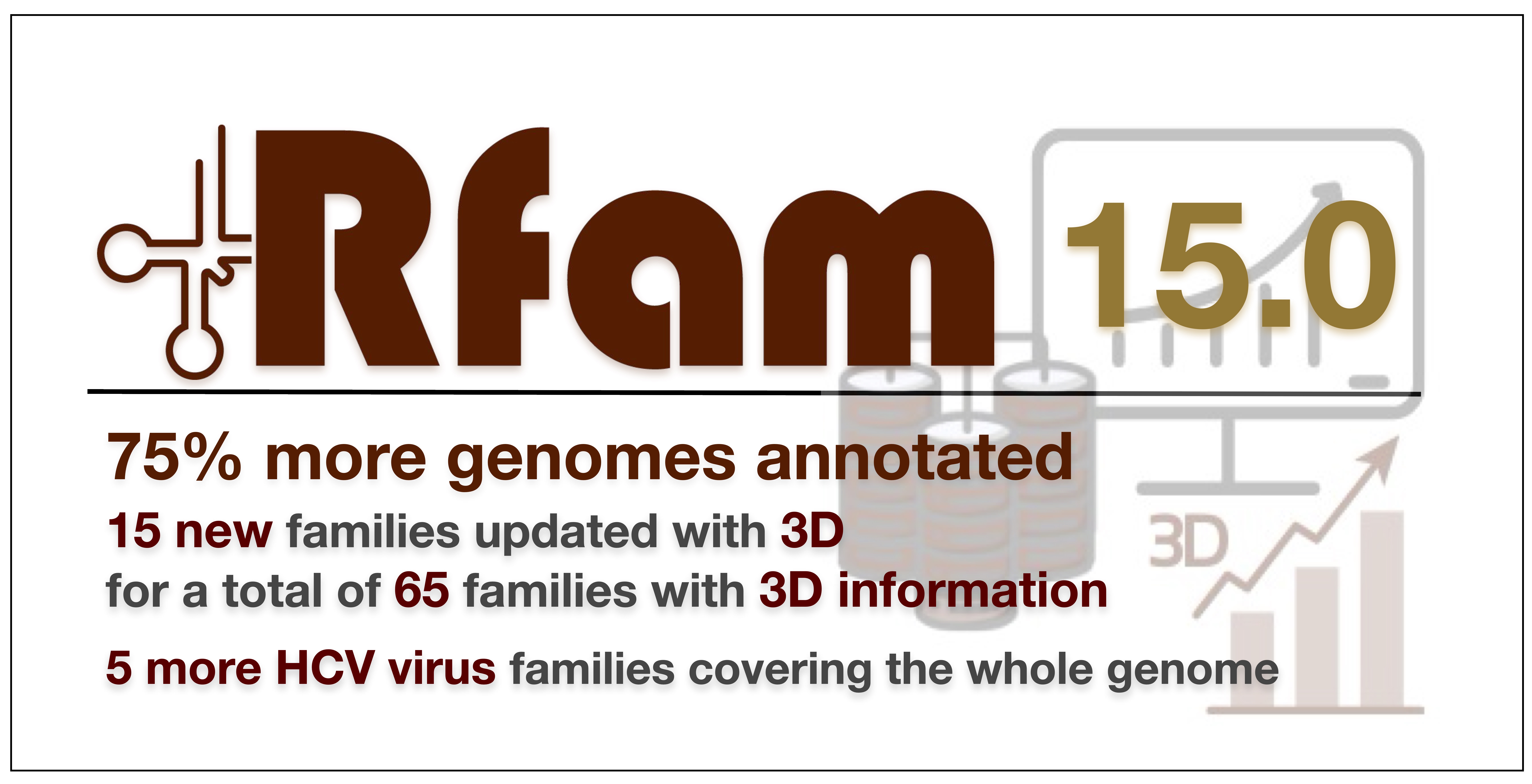
Rfam 15: RNA families database in 2025
Nucleic Acids Research (2024)
View all Rfam papers
Current projects
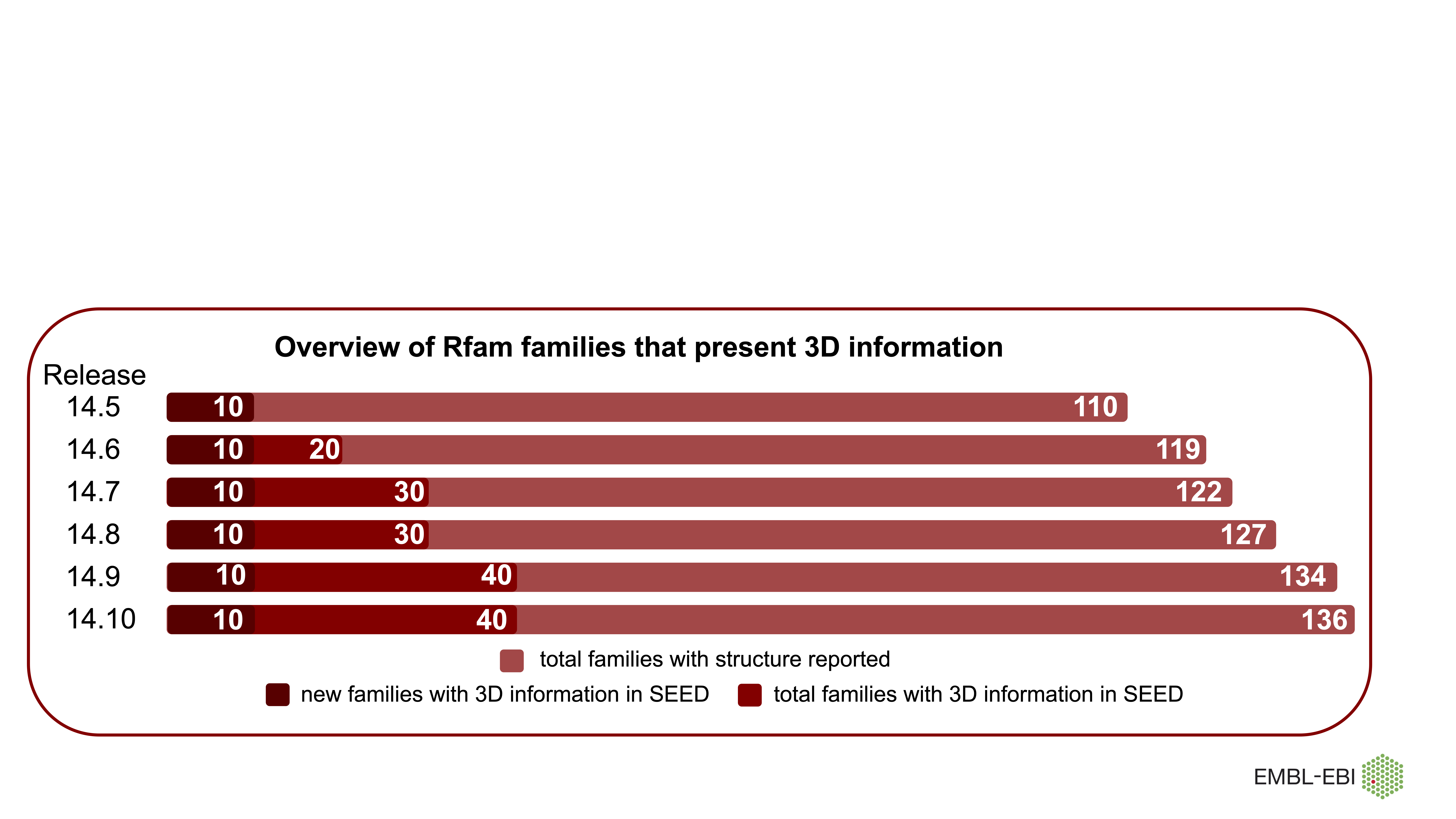
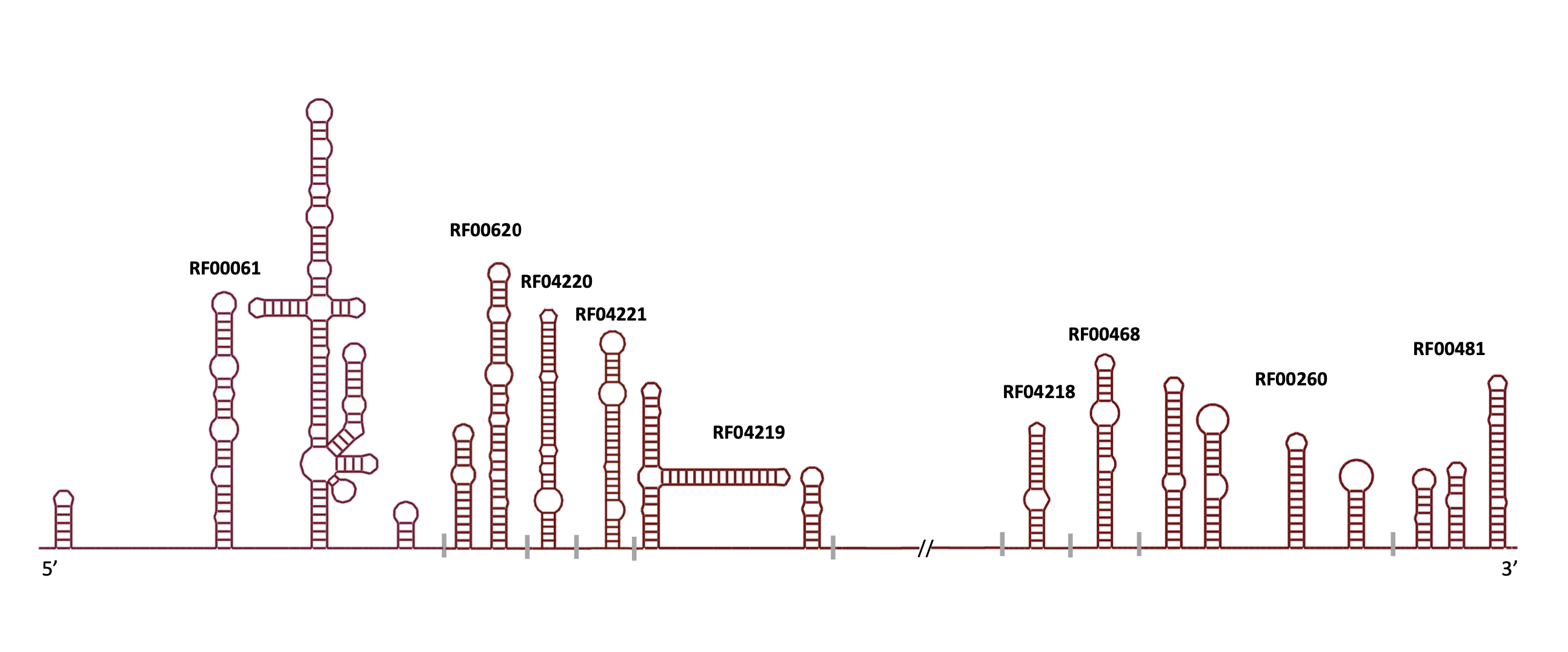
3D Families
Featured families
SAM riboswitch
The SAM riboswitch seed alignment has been revised using the 3D structure information View family →
manA RNA
The manA seed alignment has been revised using the original ZWD alignment View family →
L4-Archaeoglobi
L4-Archaeoglobi is one of the new r-leader families imported from ZWD View family →
General Flavivirus xrRNA
General Flavivirus exoribonuclease-resistant RNA element is one of the new Flavivirus RNA families View family →
LOOT RNA
LOOT RNA has been imported from ZWD View family →
Alphacoronavirus 5' UTR
Alphacoronavirus 5' UTR includes SL1, SL2, SL4, and SL5 stem loops View family →