This section shows a variety of different secondary structure
representations for this family.
More...
In this page you can view static images showing the secondary structure
of this family using a variety of colouring schemes:
Conservation (cons): this plot colours each character
by how well conserved it is. A site with 100% sequence conservation
is coloured red, 0% is violet.
Covariation (cov): this plot colours each base-pair
according to how much the corresponding nucleotides are co-varying.
A base-pair position at which every pair of nucleotides is co-variant
with respect to every other pair in the alignment gets a score of 2
and is coloured red.
Conversely, a base-pair position at every pair is anti-co-variant with
respect to every other pair (e.g. lots of mutations to
non-canonical pairs) gets a score of -2 and is coloured violet.
Further information on this metric can be found in this
document.
Sequence entropy (ent): this plot colours each
character by how under-
or over-represented the residues at the site are. Sites where one or
more nucleotides are over-represented while the other nucleotides are
either non-existent or near the background frequencies, receive
positive scores; sites where all the nucleotides are under-represented
receive negative scores. Further information on this metric can be
found in this document.
Fraction of canonical basepairs (fcbp): this plot
colours each base-pair by the percentage of canonical basepairs
(A:U, C:G, G:U) which are found in the corresponding position in the
alignment. A pair of sites with 100% canonical pairs is coloured red,
a site with 0% is violet.
Maximum parse of the covariance model (maxcm): this
plot takes the covariance model for the family and generates the
sequence with the maximum possible score for that model. Each
character is coloured by how many bits it contributes to the total
score.
Sequence: for most of the above cases, the
representative sequence used for the backbone is the most
informative sequence (MIS). Any residue that has a higher frequency
than than the background frequency is projected into the
IUPAC redundancy codes.
Normal: this plot simply colours each stem loop
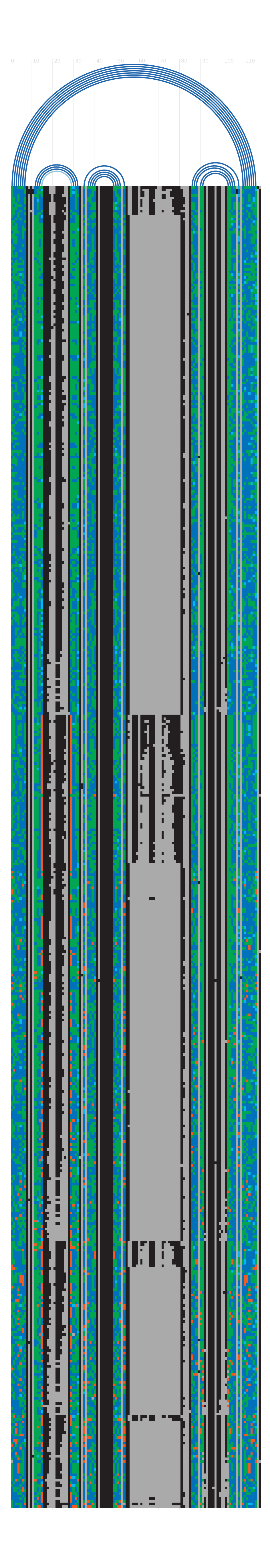
R-chie (rchie): arc diagrams showing secondary
structure, calculated using the
R-chie
package. The consensus secondary structure is visualized as arc
diagrams on top of each diagram, where a basepair in an arc, connect
two columns of the block of sequences below. The block of sequences
below represent the multiple sequence alignment of the Rfam seed, where
each sequence is a horizontal strip. Sequences in the alignments are
ordered so sequences that best fit the structure are on top, and those
that do not fit as well are towards the bottom. For seed alignments
for over 500 sequences, 500 random sequences were chosen. Rfam entries
without sturcture have a blank plot. Colour information can be found
on the R-chie
FAQ.
You can also view the secondary structure in the VARNA applet. The
applet is shown in a separate pop-up window.
Acknowledgements
The bulk of the code for generating these graphics was kindly supplied
by Andreas Gruber and Ivo Hofacker. The statistics were implemented by
Rfam.
The VARNA applet is developed by
Yann Ponty
et al:
The R-chie arc diagrams were calculated using
R-chie:
You can view the secondary structure of the family using the
VARNA applet.
You can see more information about VARNA iself
here.
Current Rfam structure
Loading...
R-scape optimised structure
Loading...
- Colours
- Statistically significant basepair with covariation
- 97% conserved nucleotide
- 90% conserved nucleotide
- 75% conserved nucleotide
- 50% conserved nucleotide
- Nucleotides
- R: A or G
- Y: C or U
Tip: The diagrams are interactive:
you can pan and zoom to see more details
or hover over nucleotides and basepairs.
R-scape is a method for testing
whether covariation analysis supports the presence of a conserved RNA secondary structure.
This page shows R-scape analysis of the secondary structure from the Rfam seed alignment
and a new structure with covariation support that is compatible with the same alignment.
To find out more about the method, see the R-scape paper by
Rivas et al., 2016.
The structures are visualised using R2R.
Move your mouse over the image to show details and click to show full image.

- Arc colours
- 100% canonical basepair
- 50%
- 0%
- Nucleotide colours
- Valid basepairing
- Two-sided covariation
- One-sided covariation
- Invalid
- Unpaired
- Gap
- Ambiguous
 Loading...
Loading...
