Summary
Note on Riboswitches
This Rfam family TPP (RF00059) represents an aptamer domain of a full riboswitch TPP riboswitch aptamer (THI element). Riboswitches are non-coding RNA structures that regulate gene expression in response to ligand. Each riboswitch has two main parts: the aptamer domain and the expression platform. The aptamer domain is highly conserved to precisely bind its ligand. However, the expression platform has multiple modes of gene regulation, which introduces sequence and structure variability that increases difficulty in its detection through covariance model searching. For more information see the original publications.
Wikipedia annotation Edit Wikipedia article
The Rfam group coordinates the annotation of Rfam families in Wikipedia. This family is described by a Wikipedia entry TPP riboswitch. More...
This page is based on a Wikipedia article. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
Sequences
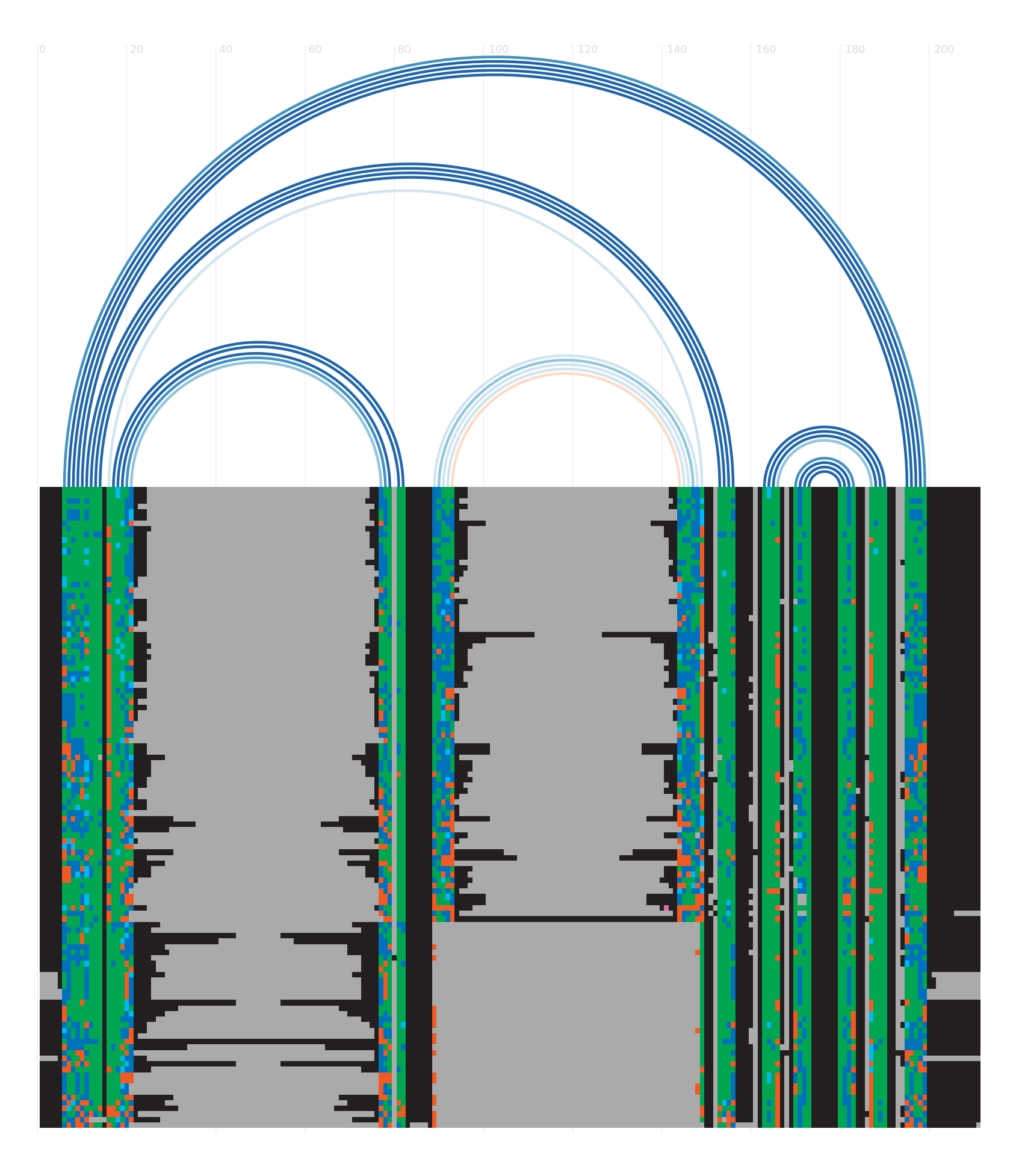
Alignment
Seed alignment view
Download
Download a gzip-compressed, Stockholm-format file containing the seed alignment for this family. You may find RALEE useful when viewing sequence alignments.
Submit a new alignment
We're happy receive updated seed alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Secondary structure
Species distribution
Sunburst controls
HideWeight segments by...
Change the size of the sunburst
Colour assignments
 Archea
Archea
|
 Eukaryota
Eukaryota
|
 Bacteria
Bacteria
|
 Other sequences
Other sequences
|
 Viruses
Viruses
|
 Unclassified
Unclassified
|
 Viroids
Viroids
|
 Unclassified sequence
Unclassified sequence
|
Selections
Click on a node to select that node and its sub-tree.
Clear selection
This visualisation provides a simple graphical representation of the distribution of this family across species. You can find the original interactive tree in the adjacent tab. More...
Tree controls
HideThe tree shows the occurrence of this RNA across different species. More...
Loading...
Please note: for large trees this can take some time. While the tree is loading, you can safely switch away from this tab but if you browse away from the family page entirely, the tree will not be loaded.
Trees
This page displays the predicted phylogenetic tree for the alignment. More...
Note: You can also download the data file for the seed tree.
Structures
For those sequences which have a structure in the Protein DataBank, we generate a mapping between EMBL, PDB and Rfam coordinate systems. The table below shows the structures on which the TPP family has been found.
Loading structure mapping...
References
This section shows the database cross-references that we have for this Rfam family.
Literature references
-
Rodionov DA, Vitreschak AG, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS J Biol Chem 2002;277:48949-48959. Comparative genomics of thiamin biosynthesis in procaryotes. New genes and regulatory mechanisms. PUBMED:12376536
-
Miranda-Rios J, Navarro M, Soberon M Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:9736-9741. A conserved RNA structure (thi box) is involved in regulation of thiamin biosynthetic gene expression in bacteria. PUBMED:11470904
-
Winkler W, Nahvi A, Breaker RR Nature 2002;419:952-956. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. PUBMED:12410317
-
Sudarsan N, Barrick JE, Breaker RR RNA 2003;9:644-647. Metabolite-binding RNA domains are present in the genes of eukaryotes. PUBMED:12756322
-
Kubodera T, Watanabe M, Yoshiuchi K, Yamashita N, Nishimura A, Nakai S, Gomi K, Hanamoto H FEBS Lett 2003;555:516-520. Thiamine-regulated gene expression of Aspergillus oryzae thiA requires splicing of the intron containing a riboswitch-like domain in the 5'-UTR. PUBMED:14675766
-
Serganov A, Polonskaia A, Phan AT, Breaker RR, Patel DJ Nature. 2006;441:1167-1171. Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch. PUBMED:16728979
-
Welz R, Breaker RR RNA. 2007;13:573-582. Ligand binding and gene control characteristics of tandem riboswitches in Bacillus anthracis. PUBMED:17307816
-
Lee K, Huang X, Yang C, Lee D, Ho V, Nobuta K, Fan JB, Wang K PLoS One. 2013;8:e70720. A genome-wide survey of highly expressed non-coding RNAs and biological validation of selected candidates in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. PUBMED:23950988
-
Thore S, Leibundgut M, Ban N Science. 2006;312:1208-1211. Structure of the eukaryotic thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch with its regulatory ligand. PUBMED:16675665
-
Welz R, Breaker RR RNA. 2007;13:573-582. Ligand binding and gene control characteristics of tandem riboswitches in Bacillus anthracis. PUBMED:17307816
-
Serganov A, Polonskaia A, Phan AT, Breaker RR, Patel DJ Nature. 2006;441:1167-1171. Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch. PUBMED:16728979
-
Edwards TE, Ferre-D'Amare AR Structure. 2006;14:1459-1468. Crystal structures of the thi-box riboswitch bound to thiamine pyrophosphate analogs reveal adaptive RNA-small molecule recognition. PUBMED:16962976
-
Thore S, Frick C, Ban N J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:8116-8117. Structural basis of thiamine pyrophosphate analogues binding to the eukaryotic riboswitch. PUBMED:18533652
-
Kulshina N, Edwards TE, Ferre-D'Amare AR RNA. 2010;16:186-196. Thermodynamic analysis of ligand binding and ligand binding-induced tertiary structure formation by the thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch. PUBMED:19948769
-
Warner KD, Homan P, Weeks KM, Smith AG, Abell C, Ferre-D'Amare AR Chem Biol. 2014;21:591-595. Validating fragment-based drug discovery for biological RNAs: lead fragments bind and remodel the TPP riboswitch specifically. PUBMED:24768306
External database links
| Gene Ontology: | GO:0030976 (thiamine pyrophosphate binding); |
| Sequence Ontology: | SO:0000035 (riboswitch); |
Curation and family details
This section shows the detailed information about the Rfam family. We're happy to receive updated or improved alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Curation
| Seed source | Vitreshchak A | ||||||
| Structure source | Published; PMID:12376536; | ||||||
| Type | Cis-reg; riboswitch; | ||||||
| Author |
Rodionov DA ,
Vitreshchak AG,
Mironov AA,
Gelfand MS ,
Vitreshchak AG,
Mironov AA,
Gelfand MS ,
Bateman A ,
Bateman A ,
Moxon SJ ,
Moxon SJ ,
Ontiveros-Palacios N ,
Ontiveros-Palacios N
|
||||||
| Alignment details |
|
Model information
| Build commands |
cmbuild -F CM SEED
cmcalibrate --mpi CM
|
| Search command |
cmsearch --cpu 4 --verbose --nohmmonly -T 30.00 -Z 2958934 CM SEQDB
|
| Gathering cutoff | 54.3 |
| Trusted cutoff | 54.3 |
| Noise cutoff | 54.2 |
| Covariance model | Download |
 Loading...
Loading...