Summary
Wikipedia annotation Edit Wikipedia article
The Rfam group coordinates the annotation of Rfam families in Wikipedia. This family is described by a Wikipedia entry MicroRNA. More...
This page is based on a Wikipedia article. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
Sequences
Alignment
Seed alignment view
Download
Download a gzip-compressed, Stockholm-format file containing the seed alignment for this family. You may find RALEE useful when viewing sequence alignments.
Submit a new alignment
We're happy receive updated seed alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
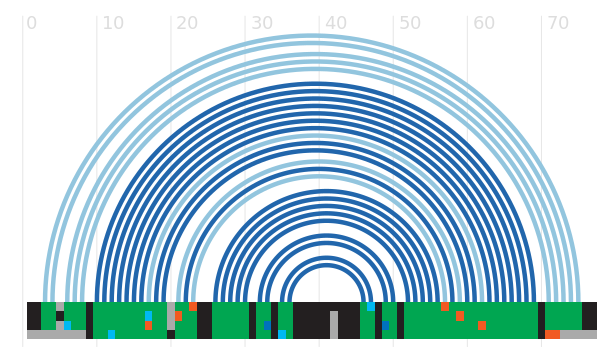
Secondary structure
Species distribution
Sunburst controls
HideWeight segments by...
Change the size of the sunburst
Colour assignments
 Archea
Archea
|
 Eukaryota
Eukaryota
|
 Bacteria
Bacteria
|
 Other sequences
Other sequences
|
 Viruses
Viruses
|
 Unclassified
Unclassified
|
 Viroids
Viroids
|
 Unclassified sequence
Unclassified sequence
|
Selections
Click on a node to select that node and its sub-tree.
Clear selection
This visualisation provides a simple graphical representation of the distribution of this family across species. You can find the original interactive tree in the adjacent tab. More...
Tree controls
HideThe tree shows the occurrence of this RNA across different species. More...
Loading...
Please note: for large trees this can take some time. While the tree is loading, you can safely switch away from this tab but if you browse away from the family page entirely, the tree will not be loaded.
Trees
This page displays the predicted phylogenetic tree for the alignment. More...
Note: You can also download the data file for the seed tree.
References
This section shows the database cross-references that we have for this Rfam family.
Literature references
-
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP; Science. 2001;294:858-862. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. PUBMED:11679671
-
Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG, Abdelhakim A, Yekta S, Rhoades MW, Burge CB, Bartel DP; Genes Dev. 2003;17:991-1008. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. PUBMED:12672692
-
Ruby JG, Jan C, Player C, Axtell MJ, Lee W, Nusbaum C, Ge H, Bartel DP; Cell. 2006;127:1193-1207. Large-scale sequencing reveals 21U-RNAs and additional microRNAs and endogenous siRNAs in C. elegans. PUBMED:17174894
-
Kato M, de Lencastre A, Pincus Z, Slack FJ; Genome Biol. 2009;10:R54. Dynamic expression of small non-coding RNAs, including novel microRNAs and piRNAs/21U-RNAs, during Caenorhabditis elegans development. PUBMED:19460142
-
Zisoulis DG, Lovci MT, Wilbert ML, Hutt KR, Liang TY, Pasquinelli AE, Yeo GW; Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17:173-179. Comprehensive discovery of endogenous Argonaute binding sites in Caenorhabditis elegans. PUBMED:20062054
-
Warf MB, Johnson WE, Bass BL; RNA. 2011;17:563-577. Improved annotation of C. elegans microRNAs by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer. PUBMED:21307183
-
Chung WJ, Agius P, Westholm JO, Chen M, Okamura K, Robine N, Leslie CS, Lai EC Genome Res. 2011;21:286-300. Computational and experimental identification of mirtrons in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. PUBMED:21177960
-
de Lencastre A, Pincus Z, Zhou K, Kato M, Lee SS, Slack FJ Curr Biol. 2010;20:2159-2168. MicroRNAs both promote and antagonize longevity in C. elegans. PUBMED:21129974
-
de Wit E, Linsen SE, Cuppen E, Berezikov E; Genome Res. 2009;19:2064-2074. Repertoire and evolution of miRNA genes in four divergent nematode species. PUBMED:19755563
-
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D155. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. PUBMED:30423142
External database links
| Gene Ontology: | GO:0016442 (RISC complex); GO:0035195 (miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing); |
| Sequence Ontology: | SO:0001244 (pre_miRNA); |
| MIPF: | MIPF0000237 |
Curation and family details
This section shows the detailed information about the Rfam family. We're happy to receive updated or improved alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Curation
| Seed source | Griffiths-Jones SR | ||||||
| Structure source | Predicted; RNAalifold | ||||||
| Type | Gene; miRNA; | ||||||
| Author |
Griffiths-Jones SR
|
||||||
| Alignment details |
|
Model information
| Build commands |
cmbuild -F CM SEED
cmcalibrate --mpi CM
|
| Search command |
cmsearch --cpu 4 --verbose --nohmmonly -T 30.00 -Z 2958934 CM SEQDB
|
| Gathering cutoff | 60.0 |
| Trusted cutoff | 64.7 |
| Noise cutoff | 50.5 |
| Covariance model | Download |
 Loading...
Loading...